 Text messages are still central to communication on smartphones, but users and companies alike want new functions for messages. These are provided by “Rich Communication Services” (RCS), a new standard in messenger communication that goes beyond the decades-old SMS standard. What are the differences between the two and what are their advantages and disadvantages?
Text messages are still central to communication on smartphones, but users and companies alike want new functions for messages. These are provided by “Rich Communication Services” (RCS), a new standard in messenger communication that goes beyond the decades-old SMS standard. What are the differences between the two and what are their advantages and disadvantages?
How does SMS work?
SMS have been the standard for text messages for decades, sent via the mobile network without needing access to WiFi or a data network. Every day, 23 to 27 billion text messages are sent worldwide. Despite their limited functions compared to other messenger services (only text can be sent, no group chats and no end-to-end encryption are available), SMS is still widely used.
MMS was an extension of SMS, allowing images, audio, and video files to be transferred but had very severe restrictions in terms of file size. However, these are now only used in the USA.
What are the features of RCS?
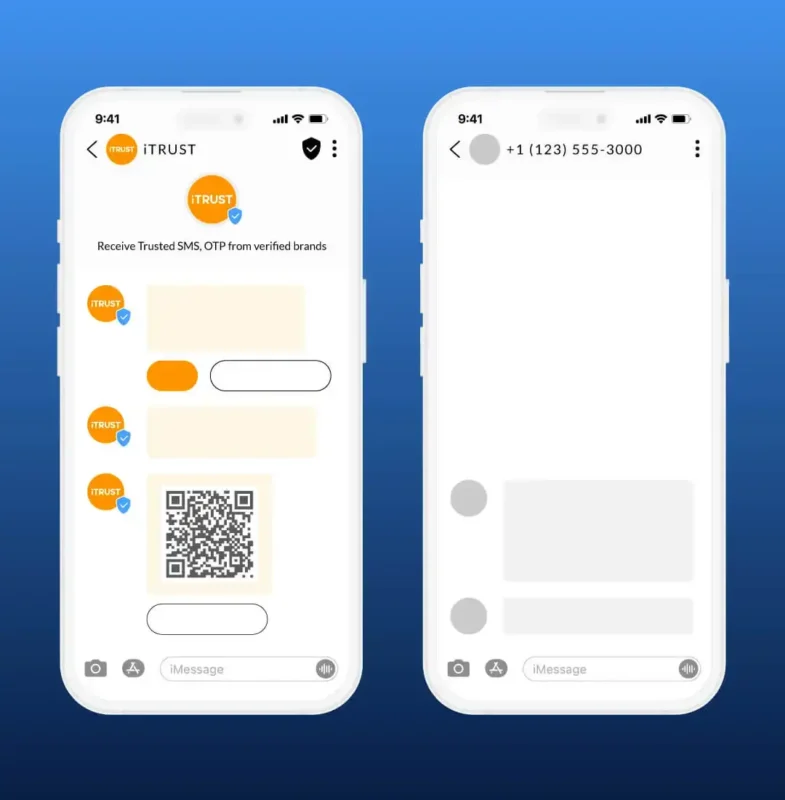
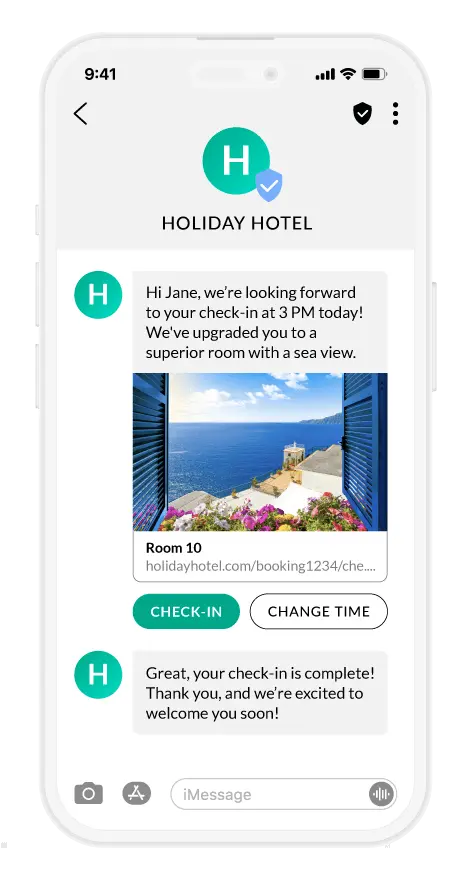
RCS offers new functions and security features that SMS does not have. RCS and messaging services such as WhatsApp, Signal, Telegram, or Facebook Messenger are IP-based—they are referred to as over-the-top (OTT) platforms. RCS is an open standard, meaning that basically any device can use it, with only a connection to Wi-Fi or a 4G/LTE/5G IP network service required.
What are the advantages of RCS?
Multimedia content: With RCS you can send pictures, videos, GIFs, location data, and more
Group chats: Easily create and manage group conversations.
Read receipts: Users can see if their message has been read.
Security features: Encryption and verification of messages before delivery.
No app required: RCS is available directly via the messenger apps on smartphones (unlike other OTT messenger services), which means easier usability and direct availability.
Where is RCS available?
Smartphones with Android 5.0 or higher can access RCS, and just needs to be activated (in device settings or message settings, depending on the model). Messenger clients such as the “Google Messages App” are now pre-installed on most current smartphones. Since iOS 18, RCS is also supported in the Apple Messages app. Most telecommunications providers worldwide support RCS, including Verizon, T-Mobile, AT&T, Vodafone, and Deutsche Telekom.
Conclusion – which is better: RCS or SMS?
Because of the much greater range of functions, the use of RCS in both the private and B2C sectors will increase rapidly over the next few years. There are only restrictions on the use of RCS if no data network is available (in which case only SMS can be sent) or if the receiving device does not support RCS. In this case, the message is sent as an SMS or MMS, which incurs additional costs for the sender (although the sender is informed of this before the message is sent). In some areas with a poor data network or for users with older devices, SMS will therefore remain the standard, but that does not diminish the increasing importance of RCS.
